
Check integrity of flexor/extensor tendons in the presence of open wounds.
Substantial injuries or infected open wounds require a surgical opinion as these may require admission for IV antibiotic cover and washout in theatre.
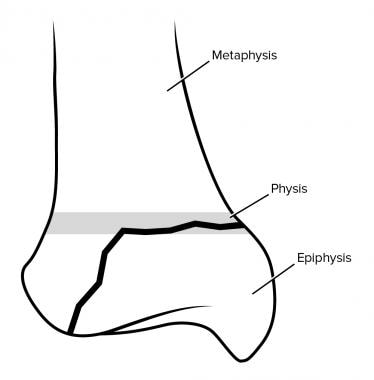
Salter harris type 3 skin#
Be vigilant for rotational deformity no degree of malrotation is acceptable.Įnsure to evaluate skin integrity over the injured area, check for and document the presence of open wounds consider the possibility that these could be so-called ‘’fight bites’’ and will require antibiotics. The child/adolescent will usually present with bruising, swelling and diffuse pain over the dorsum of the hand. This injury usually occurs as a result of direct bony trauma when the child/adolescent strikes a fixed object such as a wall with a closed fist or is struck on a fisted hand with an object such as a bat/hurl/hockey stick for example. The most common type of metacarpal fracture is the so-called ‘‘boxer’s fracture’’, which involves the neck of the ring or small finger metacarpal.

Metacarpal fractures are common in adolescent athletes. During the exam she is visibly withdrawn and quiet and you are suspicious that there is more than a hand injury bothering Katie. There is an obvious loss of knuckle height and rotational deformity to her little finger. There are no open wounds and she reports focal tenderness on palpation to her 5 th metacarpal bone. Katie shows you her right hand which is grossly swollen and bruised over the dorsal surface. Her father reports that she had an argument with her Mum and punched a wall at home, he also reports that this is not the first time an incident like this has occurred. Katie is a 15-year-old girl who presents to your ED with her father. Ask and record the child’s hand dominance as this can impact injury management. Consider injuries that are self-inflicted in the older child/adolescent age group.ĭ- Dominance. A comprehensive history is essential to detect the possibility of intentional injury from physical abuse or an unintentional injury as a result of neglect. NAI Like all paediatric injuries consider the possibility of NAI, especially in the younger child. N- Needles/Needs Tetanus? Ask about vaccinations, is the child’s Tetanus vaccination up to date, especially relevant if open wounds or animal/human bites are present. Ask about any altered sensations such as paraesthesia which could indicate a nerve injury. Ask about the child’s hobbies, sports, activities, career aspirations (in older child) as these may impact on management.Ī- Altered sensations. H- How the injury happened? Ask about mechanism of injury including the environment in which the injury was obtained. Clinical History/Documentation Essentials: Take a HAND history


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
